Updated: 19/4/2017
So related to biochemistry we will review carbohydrates for the EE, we will share the most important tips and notes related to the PEBC pharmacits evaluating exam!
Quick notes:
- Carbohydrates are the main sources of energy in the body.
- The liver has the major responsibility for maintaining blood glucose levels.
- The brain oxidizes glucose to CO2 and H2O, whereas red blood cells oxidize glucose to pyruvate and lactate.
- The digestion of carbohydrates occurs briefly in mouth and largely in the intestine.
- Carbohydrates digestion begins in the mouth to a significant extent. During the process of mastication, salivary α-amylase (ptyalin) acts on starch randomly and cleaves α- 1,4-glycosidic bonds.
- The enzyme salivary amylase is inactivated by high acidity (low pH) in the stomach. Therefore, the ongoing degradation of starch is stopped in stomach.
- Non digestible carbohydrates : The fibers are chemically complex carbohydrates which include cellulose, hemicellulose, pectins, lignin and gums. ( Usually used as laxatives).
Classification:
- Monosaccharides : Glucose and Fructos.
- Disaccharides : two monosaccharides are combined together with elimination of a water molecule example: Sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
- Oligosaccharides : from two to ten monomers.
- Polysaccharides : More than 10 monomers as in cellulose and starch.
Metabolism of Carbohydrates:
Just to know what is the metabolism and the difference between anabolism and catabolism you can refer to this article : Metabolism ( Anabolism ↔ Catabolism )
So, metabolic pathway constitutes a series of enzymatic reactions to produce specific products.
Metabolism is divided into:
- Anabolism : The biosynthetic reactions related to the formation of complex molecules from simple precursors or substrates.
- Catabolism : The degradative processes related to the breakdown of complex molecules to simpler ones, with release of energy.
How do Carbohydrates metabolized ?
There are many pathways for Carbohydrates metabolism but we will go through the most important ones:
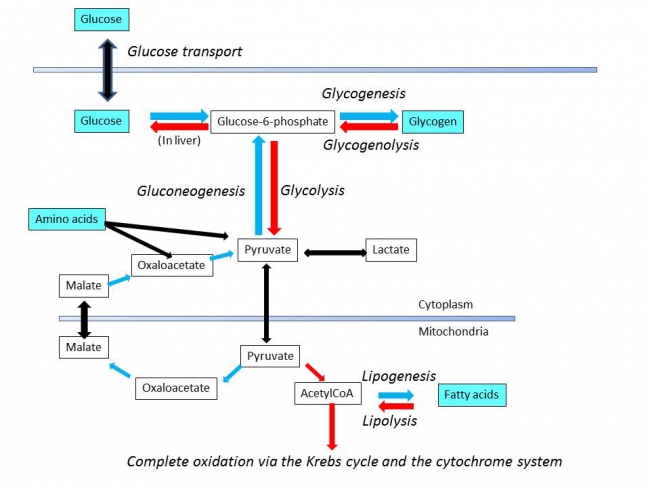
- Glycolysis (Embden-Meyerhof pathway) : The oxidation of glucose to pyruvate and lactate.
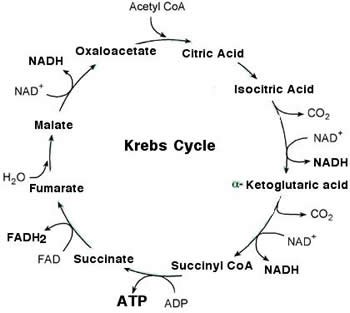
- Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle) : The oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO2. Krebs cycle is the final common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates, fats or amino acids, through acetyl CoA.
- Gluconeogenesis : The synthesis of glucose from non carbohydrate source & it is regulated by glucagon (e.g. amino acids, glycerol etc.).
- Glycogenesis : The formation of glycogen from glucose.
- Glycogenolysis : The breakdown of glycogen to glucose.
- Hexose monophosphate shunt (pentose phosphate pathway or direct oxidative pathway) : This pathway is an alternative to glycolysis and TCA cycle for the oxidation of glucose (directly to carbon dioxide and water).
Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle:
- The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid—TCA cycle) is the most important metabolic pathway for the energy supply to the body.
- Citric acid cycle essentially involves the oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO2 and H2O.
- Krebs cycle is the most important central pathway connecting almost all the individual metabolic pathways.
- The enzymes of TCA cycle are located in mitochondrial matrix, in close proximity to the electron transport chain. This enables the synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation without any hindrance.
- The cycle operates only under aerobic conditions.