Phases of the Cardiac Cycle :
♥♥ The action potential of the heart consists of 5 phases , from 0 to 4 ♥♥
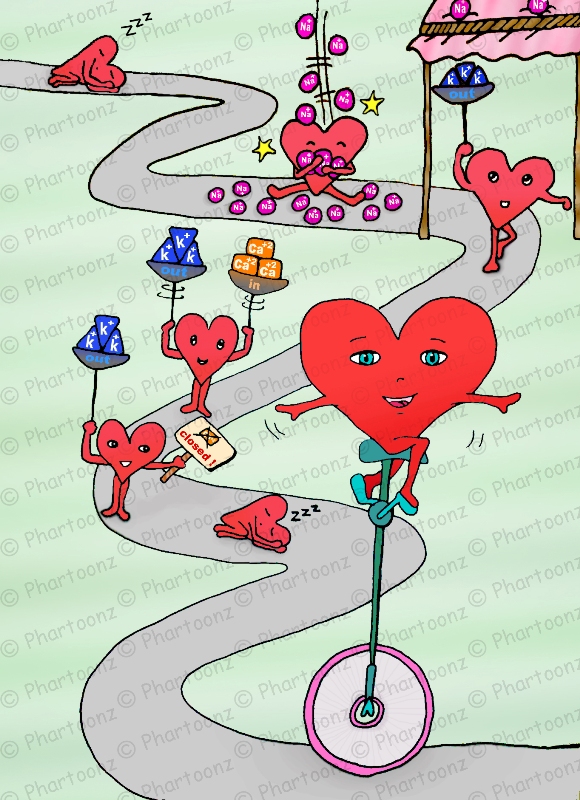
Ι – Phase 4 : ” resting polarized cells “
– This phase of action potential is associated with diastole of the chamber of the heart.
at that time , the inside is more negative than the outside & the cells are resting & ready to receive an electrical stimulus
Hint :
– Phase Four appears as a flat line ( ___ ) in ECG , which resembles Rest ” ( _______ :sleeping: zZzZzZz ) “



ΙΙ- Phase 0 : ” upstroke ↑ + fast depolarization “
– This phase is due to the opening of the fast Na+ channels causing Na+ ions to Rush into the cells , increasing the positive charges inside the cells .
– the cells depolarize rapidly and begin to contract
– it is characterized by a sharp, tall upstroke of the action potential on the ECG chart .



ΙΙΙ- Phase 1 : ” spike + a little bit repolarization “
– inactivation of the fast Na+ channels occurs & the cell begins an early partial repolarization
this early repolariztion is due to the movement of K+ Out of the cell so the cell starts to become less positive in the inside
– contraction is still in process



ΙV – Phase 2 : ” plateau “
– This plateau phase of the cardiac action potential is sustained by a balance between inward movement of Ca2+ and outward movement of K+



V- Phase 3 : ” down slope ↓ + Fast repolarization “
– Rapid repolarization occurs to return to the resting polarized phase 4 again .
the Ca2+ channels close so no ca ions can no longer enter to the cells , while the K+ channels are still open so K+ can keep getting out of the cell .
This ensures a net outward current of positive charges , until the membrane is completely polarized ( more -ve inside & more +ve out side )
Hint : repolarization is complete by the end of phase 3 😉
after that , the Phases of the Cardiac Cycle are repeated with each electric shot fired from the Heart pacemakers .
Hint :
It’s more easier to study action potentials when you first memorize the Ion which plays the most important rule in each phase
– Na+ mainly in phase 0 ( notice that Na is one letter different that No ! .. & o = 0 ” zero ” :happy: )
– Ca2+ mainly in phase 2 ( notice that both valency of calcium and the phase number = 2 ) 😉
– K+ mainly in phase 1 , 3 , 4 ( notice that 1+3=4 😎 )
Play with this animation cool animation 😎 , try to compare between the in&outflux on ions and the chart :
Hint :
the dark yellow channel is for Na+
the light yellow channel is for Ca+2
the red channels are for K+




Extra information > > > special phases :
*1* – Absolute refractory period;
– it’s a period in which no stimulus -no matter how strong- can cause another depolarization
*2* – Relative refractory period :
– the cell has partially repolarized, so Only a very strong stimulus could cause a depolarization
*3* – Super normal period (SNP) :
it’s a period in which a stimulus weaker than normally required can cause a depolarization
– it is rare and not normal in a healthy heart .

——–
References :
– Essentials of Human Physiology for Pharmacy
– Netter atlas of Physiology
– The free medical dictionary official web site

Thanks for the info
Good article
It took me a long time to search on the net, only your site explain the fully details, bookmarked and thanks again.
– Kris
welcome everyone :happy:
Beautiful write-up; thanks 🙏