Why is it difficult to remember MABs?
In pharmacology, we used to remember pharmacological classes by their suffix “ends”. For example, (Captopril, Ramipril, lisinopril) are all ending with -pril so we know that these drugs are related to ACEI and then we can predict their mechanism of action just from their name. However, this is not the case with drugs or molecules that ends with -mab and they are known as Monoclonal Antibodies.
What are Monoclonal Antibodies?
For the sake of simplicity, Monoclonal Antibodies is a kind of targeted therapy. If you know how our immune system work, it will be easy for you to understand the general concept of Monoclonal Antibodies.
Imagine a foreign particle like a virus hijacked your system. An immune response or reaction will occur against this virus “Antigen” and your body is smart enough to produce antibodies to recognize and enhance your own defense system in the future if you are attacked again.
Using the same concept, scientists were able to produce monoclonal antibodies in labs that are very specific to part of the antigen to treat many diseases including cancer.
For example, in cancer treatment, chemotherapy was the traditional way to manage tumors or cell over growth. However, one of the major problems of this treatment is that it is not specific to cancerous cells and can trigger a lot of adverse effects.
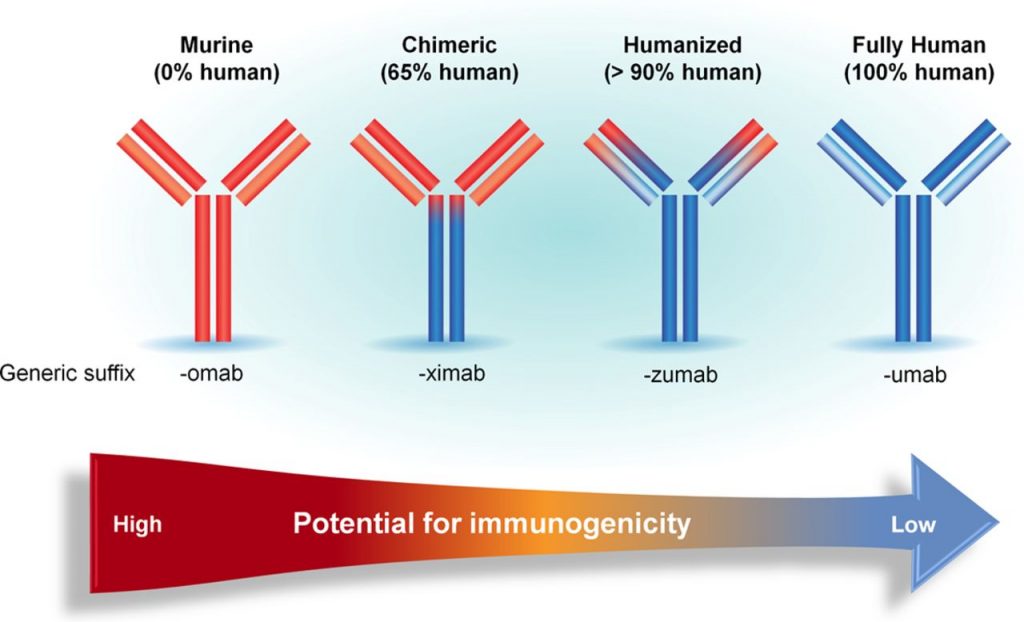
There are many ending of Monoclonal Antibodies “MABs”:
List of mnemonic to remember monoclonal antibodies nomenclature (Prefix and suffix examples) :
| Suffix – Nomenclature guide | Source + targeted therapy |
| -omab | Murine |
| –ximab | Chimeric |
| –zumab | Humanized |
| –umab | Fully Human |
| –tu xx mab | tumor directed xx Monoclonal Antibody |
| –li xx mab | immune directed xx Monoclonal Antibodies |
| –ci xx mab | cardiovascular directed xx Monoclonal Antibodies |
| –vi xx mab | virus directed xx Monoclonal Antibodies |
| –ki xx mab | interleukin directed xx Monoclonal Antibodies |
| –to xx mab | Toxin directed xx Monoclonal Antibodies |
| –os mab | Bone directed xx Monoclonal Antibodies |
How to remember the most popular Monoclonal Antibodies and their MOA?
Now it is the mnemonics part, this is how we save things in our brains – using the previous table will make our life a bit easy-
Denosumab:
back to the above table: OS is related to bone … and we can pronounce it dense … it means enhance the density of bones … so it is used in the treatment of osteoporosis and from the name it is fully human –umab.
Pretty easy?
Abciximab:
Ab: Antiplatelet aggregation (binds to the glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor of human platelets and inhibits platelet aggregation by preventing the binding of fibrinogen)
ci: cardiovascular directed … confirmed because it is a platelet aggregation inhibitor
ximab: chimeric
INFliximab:
INF: it is like TNF .. Tumer necrosis factor inhibitor.
Li: immuno directed
ximab: chimeric
Trastuzumab:
For patients with invasive breast cancers that overexpress HER2.
Tu: tumor directed, used in breast cancer
Zumab: Humanized
Here below are list of the most popular MABs:
- basiliximab
- rituximab
- bevacizumab
- cetuximab
- Panitumumab
- alirocumab
- tocilizumab
- adalimumab
- ustekinumab
- golimumab
- natalizumab
- omalizumab
- idarucizumab

Very well explained good job